An analysis by Dawn Smith of the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reported at the 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI 2013) on 4 March has provided the first estimate of the efficacy of condoms in preventing HIV transmission during anal sex since 1989.
UK: Updated guidance on HIV transmission, the law and the work of the clinical team now published
The British HIV Association (BHIVA) and the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) have produced updated guidance on HIV Transmission, the Law and the Work of the Clinical Team.
This guidance is aimed at those working in the field of HIV medicine, especially clinicians, but will also be of use to general practitioners and people living with HIV who want to understand the legal and medical basis for some of their care decisions.
The guidance begins with a clear statement against HIV criminalisation:
BHIVA and BASHH believe that this use of the law is unhelpful and potentially harmful to public health and support UNAIDS recommendations to limit the use of criminal law and the Oslo declaration view that a “non-punitive, non-criminal HIV prevention approach” is preferable.
Covering the law in England & Wales as well as Scotland, the document aims to provide information and guidance on managing issues related to sexual transmission of HIV based on current scientific evidence. It applies generic ethical and professional principles but with a greater emphasis on providing a confidential environment in which extremely sensitive matters can be frankly and fully discussed. This enables appropriate care of people with HIV and benefits public health by encouraging individuals to access testing and treatment. Within this framework this document sets out the roles and responsibilities of health care professionals when caring for individuals living with HIV.
Consistent with the recent BHIVA and the Expert Advisory Group on AIDS (EAGA) position statement on the use of antiretroviral therapy to reduce HIV transmission, the guidance notes:
In most situations the appropriate use of antiretroviral treatment is at least as effective as condoms in preventing sexual transmission of HIV. This is accepted by the [Crown Prosecution Service of England and Wales] and [Scottish Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service] so it is likely that evidence showing that the defendant was taking effective antiretroviral treatment at the time of the alleged transmission may be used to demonstrate that they were not reckless.
The guidance also clearly states that healthcare professionals “must be mindful of their duty not to work beyond their expertise in legal matters. For people with HIV, advice must include the routes of HIV transmission and how to prevent transmission, with information about safer sexual practices, the use of condoms and suppression of viral load. Advice must be given in a non-judgmental way.”
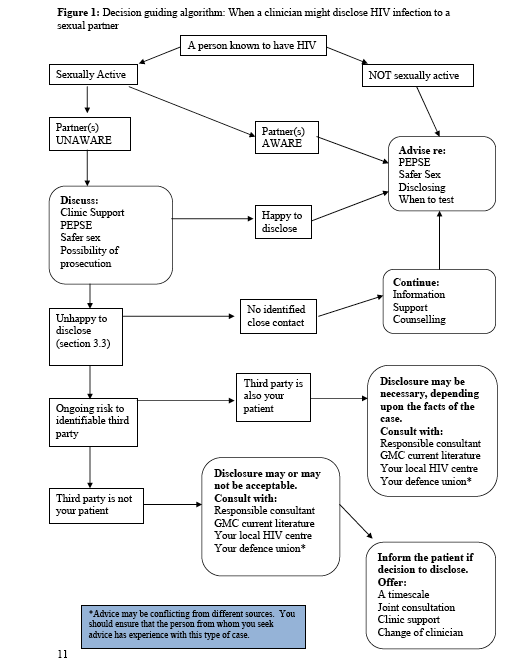
It also discusses issues of confidentiality, noting that “it is important when considering breaching confidentiality to weigh up all potential harms as there may be situations where disclosure of HIV status to protect a sexual partner results in considerable harm to an individual e.g. domestic violence. In situations where a health care professional believes that an HIV positive individual continues to put sexual contacts at risk their duties and subsequent action depend upon the type of contact.” See Figure 1 below.
The guidance also clearly states that “no information should be released to the police unless patient consent has been verified or there is a court order in place, except in very limited circumstances defined by the [General Medical Council].”
Importantly, it also notes that only individuals can make complainants to the police “and health care workers should remain impartial during discussions with patients.”
Finally, it provides clear advice to both help prevent transmission of HIV to sexual partners and to avoid prosecution for ‘reckless’ HIV transmission. Accordingly, people with HIV should do at least one of the following:
- Use a male or female condom fitted correctly along with water-based lubricant. Individuals doing this are unlikely to be seen as reckless for legal purposes. In the event of a condom split, it is advisable to disclose HIV status in order to support the partner’s decision whether or not to obtain post-exposure prophylaxis (PEPSE), which should be taken within 72 hours. The need for PEPSE will depend upon the type of sexual activity and the HIV viral load. An assessment of the risk should be undertaken by a clinician according to the BASHH PEPSE guidelines. Disclosure in these situations would suggest that the person with HIV was not reckless.
- Adhere to effective (suppressed viral load) antiretroviral medication. There is growing evidence of extremely low/minimal risk of transmission when plasma HIV is fully suppressed with the use of antiretroviral medication. In some situations an undetectable viral load can afford protection equivalent to or greater than that of condoms. A person with HIV is unlikely to be seen as reckless when relying on a suppressed viral load instead of condom use if they have been counselled accordingly by an HIV clinician or similar medical authority. It is recommended that this discussion is documented in the patient’s medical records.
In addition people with HIV should be advised that disclosure of HIV positive status to a partner before sex is important to support informed agreement around risk and safer sex behaviours. To avoid successful prosecution an individual who is not taking effective antiretroviral medication and does not use a condom must disclose their HIV status to sexual partners before sex takes place.
The entire guidance is reproduced below.
British public confused about how you get HIV
PUBLIC CONFUSED ABOUT HOW YOU GET HIV Nearly half (46%) of the general public wrongly think you can get HIV from being bitten, spat at or coming into contact with a discarded needle and underestimate the impact unsafe sex has on HIV transmission, a new survey[1] shows (14 Jan) .
Austria: HIV-positive man aquitted for ‘oral sex without ejaculation’ (Update)
Update: December 18th
A gay man on trial for allegedly exposing his ex-partner to HIV during ‘oral sex without ejaculation’ has been acquitted. The judge told the 37 year-old defendant that he had acted “entirely properly” according to Austria’s ‘safer sex’ guidance.
The case is covered in several Austrian newspapers, including Der Kurier and Der Standard, as well as the gay news portal, GGG.at.
It centred around a complaint following the end of a short-lived relationship between summer 2008 and spring 2009. The defendant was diagnosed HIV-positive during the relationship and waited several months to disclose this to the complainant. However, since he was counselled by his doctor that insertive oral sex without ejaculation would not expose his partner to HIV, and this was the only sexual risk at issue, his defence was that he had followed Austria’s ‘safer sex’ guidance.
Defence laywer, Helmut Graupner, told the court: “They are attempting to criminalise people who do exactly what the state wants them. This accusation is simply a scandal.”
(Under Articles 178 and 179 of Austria’s criminal code, disclosure is not a defence to potential HIV exposure, and so this case was not about non-disclosure, per se, but rather about whether the complainant was, in fact, exposed to HIV via oral sex without ejaculation.)
The complainant claimed on the witness stand that he had suffered mental anguish due to the fear of acquiring HIV, and he had brought the case partially because he wanted compensation for this.
However, Judge Eva Brandstetter agreed with the defence that ‘safer sex’ guidance was followed. It was “very clear that you behaved entire properly,” she told the defendant as she acquitted him.
The prosecution has until Friday to appeal the acquittal.
Original post: December 14th
Austria’s leading HIV and human rights lawyer has strongly criticised both Vienna’s prosecutorial authorities and the Austrian Ministry of Justice for allowing the forthcoming trial of an HIV-positive man for practising safer sex – namely, “oral sex without ejaculation”.
“The state must not criminalise HIV-positives for complying with the safer sex rules propagated by the same state“, says Dr. Helmut Graupner, president of Austria’s LGBT civil rights organisation Rechtskomitee LAMBDA (RKL) – who is also serving as counsel for the defendant – in a strongly-worded press release (see below). “This prosecution not only constitutes a serious human rights violation but also poses a considerable threat to public health.”
In addition Austrian MP Petra Bayr has tabled a parliamentary question to the Ministry of Justice concerning this ridiculous prosecution which asks:
- whether Parliament is aware of this prosecution;
- what it intends to do to ensure that prosecutors are aware of HIV tranmisssion risks and science;
- how it can justify HIV-related prosecutions under articles 178 and 179 of the criminal code when UNAIDS recommends against such prosecutions and asks whether Parliament will consider amending these articles to reflect up-to-date science; and
- what measures are being considered by the Justice Department to ensure consistent and science-based jurisprudence that promotes public health.
This is the second prosecution this year for perceived HIV exposure that, in fact, posed no risk whatsoever. In March 2012, a 17 year-old boy was convicted of HIV exposure after his 16 year-old girlfriend performed oral sex on him without him first disclosing that he was living with HIV. The judge said that even oral sex with condom would have been criminal as the use of condoms would not diminish the risk of infection.
The trial will take place this Monday, 17 December 2012, in room 307 at the Vienna Regional Criminal Court, Wickenburggasse 22, 1080 Vienna. Rechtskomitee LAMBDA’s press release notes that the trial is public which suggests that concerned HIV advocates could attend the trial to support the defendant (who cannot be named) and to show the prosecutor and judge that such prosecutions are out of step with science and do nothing for HIV justice.
The full Rechtskomitee LAMBDA’s press release can be downloaded here and is also reproduced below.
Austria: HIV-positive Man Prosecuted for Safer Sex
Trial next Monday in Vienna
An HIV-positive man stands criminal trial next week for practising safer sex propagated by the state and by the publicly funded aids service organisations. The prosecutor indicted him for “oral sex without ejaculation” (!), exactly what has been propagated as safer sex for decades.
The prosecution relies on Art. 178 of the Criminal Code (“wilful endangering of human beings by transmittable diseases”), an offence which for two decades had been used to convict persons (mostly women) even for sexual intercourse using a condom.
1997 the Supreme Court at last held that sexual intercourse with a condom is in accordance with the safer sex rules and no criminal offence (OGH 25.11.1997, 11 Os 171/97). And 2003 it was only after years of reopening-proceedings that the Graz Appeals Court to quash the conviction of an hiv-positive man for oral sex without ejaculation (Carinthian Oral Sex Case: http://www.RKLambda.at/news_safersex.htm). Already these days Austria´s then Minister for Health, Herbert Haupt, had stated, “that criminal persecution and conviction of hiv-positive persons for sexual contacts with hiv-negative persons in spite of them complying with the health authorities’ and aids-service-organisations´ safer sex rules run counter to effective hiv- and Aids-prevention (2313/AB XXI.GP, http://www.parlament.gv.at/PAKT/VHG/XXI/AB/AB_02313/).
Threat to effective HIV-prevention
Austria finds itself within the top ten worldwide regarding criminal conviction rates of hiv-positive persons (http://www.gnpplus.net/criminalisation/node/1262). Germany never had such a special offence and Switzerland recently restricted its law (which never had been as far-reaching as the Austrian one) to infection with malicious intent, thereby implementing a recommendation by the Swiss Commission on Aids (now: Swiss Commission on Sexual Health) (http://www.bag.admin.ch/hiv_aids/05464/12494/12821/, document for download on the right side). UNAIDS and the EU-Fundamental Rights Agency for years have been calling for a repeal of such criminalisation of HIV-positive persons and for restriction of criminal offences to intentional infection (http://www.unaids.org.fj/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=162:unaidsundp-policy-brief-criminalization-of-hiv-transmission-&catid=25:technical-documents&Itemid=74; http://fra.europa.eu/en/publication/2010/rights-based-approach-hiv-european-union, http://www.hivjustice.net/oslo/oslo-declaration/).
Accordingly the Austrian Minister of Justice in 2010 on the occasion of the Vienna World Aids-Conference had assured that Austrian criminal law would not criminalize sexual acts in accordance with the safer sex rules and declared that the prosecutors would be informed to this effect (4941/AB, 2 June 2010, http://www.parlament.gv.at/PAKT/VHG/XXIV/AB/AB_04941/).
Double game played by the (Minister of) Justice?
Nevertheless last spring a 17 year old juvenile has been convicted for oral sex (without the allegation of ejaculation) with the judge even claiming that the use of a condom would not have made a difference (http://vorarlberg.orf.at/news/stories/2523707/). And now in Vienna the prosecutor is indicting a man explicitly even for oral sex without (!) ejaculation, behaviour explicitly propagated by the health authorities´ and the aids-service-associations´ (http://www.aids.at/alles-uber-hivaids/wie-kann-ich-mich-schutzen/; http://www.aidshilfen.at/sie-haben-fragen-wir-haben-antworten; https://www.gesundheit.gv.at/Portal.Node/ghp/public/content/Safer_Sex.html).
The trial takes place next Monday, 17 December 2012 in room 307 at the Vienna Regional Criminal Court, Wickenburggasse 22, 1080 Vienna. The trial is public. Revealing the defendant´s identity in the media is strictly prohibited (§§ 7 & 7a Media Act).
Members of federal parliament have tabled a parliamentary question to the Ministry of Justice concerning this incredible prosecution (13275/J, 6 December 2012, http://www.parlament.gv.at/PAKT/VHG/XXIV/J/J_13275/).
“The state must not criminalise HIV-positives for complying with the safer sex rules propagated by the same state“, says Dr. Helmut Graupner, president of Austria’s LGBT civil rights organisation Rechtskomitee LAMBDA (RKL) and counsel for the defendant, “This prosecution not only constitutes a serious human rights violation but also poses a considerable threat to public health.”
Clear, concise interview on risk, legal literacy following Canadian Supreme Court decision
In a wide–ranging interview that poses difficult questions, Bob Leahy asks Toronto-based clinician/scientist Dr. Rupert Kaul about how can we interpret risk of HIV transmission in the age of undetectable viral load.
More criminalization, further marginalization: Supreme Court's HIV non-disclosure decisions create viral underclass |
This is the second in a series of blog posts about the recent Supreme Court of Canada decisions about the criminalization of HIV non-disclosure. See the first post here, in which we wrote about the perverse, negative impacts of the decision for women living with HIV.
US: Scott A. Schoettes of Lambda Legal outlines the battle being waged in U.S. courts over HIV criminalisation in POZ Magazine
Scott A. Schoettes is the HIV project director for Lambda Legal, a longtime legal champion of HIV-positive people and LGBT civil rights. He filed a brief in The People of the State of New York v. David Plunkett, an HIV criminalization case heard by the New York Court of Appeals, the highest court in the state.
US: HIV Medicine Association calls for repeal of HIV-specific laws
The HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA) of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) has issued a strong statement urging the repeal of HIV criminalisation statutes in the United States.
The HIVMA statement, which represents physicians, scientists and other health care professionals across the United States, demands the following:
- An end to punitive laws that single out HIV infection and other STIs and that impose inappropriate penalties for alleged non-disclosure, exposure and transmission
- All state and federal policies, laws and regulations to be based on scientifically accurate information regarding HIV transmission routes and risk;
- A federal review of all federal and state laws, policies, and regulations regarding the criminal prosecution of individuals for HIV-related offences to identify harmful policies and federal action to mitigate the impact of these laws, including the repeal of these laws and policies or guidance for correcting harmful policies; and
- Promotion of public education and understanding of the stigmatising impact and negative clinical and public health consequences of criminalisation statutes and prosecutions.
The HIVMA statement is another extremely important development in the Positive Justice Project’s campaign to repeal HIV-specific criminal laws in the United States.
In March 2011, the National Alliance of State and Territorial AIDS Directors (NASTAD) – a highly-respected organisation of public health officials that administer state and territorial HIV prevention and care programmes throughout the US – issued a similar statement.
The full HIVMA statement, which can be downloaded here, is published below.
HIVMA URGES REPEAL OF HIV-SPECIFIC CRIMINAL STATUTES
(Approved: October 16, 2012)
The HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA) of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) represents physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who practice on the frontline of the HIV/AIDS pandemic. HIVMA strongly advocates public policies that are grounded in the science that has provided the tools and knowledge base to envision a world without AIDS.
Stigma and discrimination continue to be major impediments to the comprehensive response necessary to address the HIV public health crisis. Policies and laws that create HIV-specific crimes or that impose penalties for persons who are HIV- infected are unjust and harmful to public health around the world.
In the U.S., HIV criminalization has resulted in unacceptable human rights violations, including harsh sentencing for behaviors that pose little to no risk of HIV transmission. Thirty-two states and two U.S. territories have HIV-specific criminal statutes. Thirty-two states have arrested or prosecuted individuals with HIV infection for consensual sex, biting and spitting. These laws and prosecutions unfairly target individuals with HIV infection and are not based on the latest scientific knowledge regarding HIV transmission, including the finding that transmission risk from biting or spitting is negligible.
Individuals with HIV infection can live healthy lives and approach near normal life expectancies with access to HIV care. Early diagnosis and effective management of HIV infection not only improves clinical outcomes for infected individuals but significantly reduces their risk of transmitting the virus to others. Laws that criminalize HIV infection discourage individuals from learning their HIV status and from receiving care. In doing so, they jeopardize the lives of HIV-infected individuals and place more individuals at risk of contracting an infectious disease that remains fatal if untreated.
HIV-specific criminalization fuels the stigma associated with HIV infection that slows efforts to combat the disease. Despite the availability of highly effective treatment for HIV infection, of the 1.1 million individuals living with HIV infection in the U.S., nearly 20 percent remain undiagnosed, only 37 percent are in care and just 25 percent have undetectable levels of the virus in their blood which makes it unlikely for them to be infectious to others.
All individuals must take responsibility for protecting themselves from HIV infection and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). All persons engaging in unprotected or potentially risky sexual behavior are encouraged to discuss and disclose HIV and STI status except in situations where disclosure poses a risk of harm.
HIVMA Position:
HIVMA urges a coordinated effort to address and repeal unjust and harmful HIV criminalization statutes. We support the following:
- An end to punitive laws that single out HIV infection and other STIs and that impose inappropriate penalties for alleged nondisclosure, exposure and transmission;
All state and federal policies, laws and regulations to be based on scientifically accurate information regarding HIV transmission routes and risk;
- A federal review of all federal and state laws, policies, and regulations regarding the criminal prosecution of individuals for HIV-related offenses to identify harmful policies and federal action to mitigate the impact of these laws, including the repeal of these laws and policies or guidance for correcting harmful policies; and
- Promotion of public education and understanding of the stigmatizing impact and negative clinical and public health consequences of criminalization statutes and prosecutions.
Norway: Long awaited Law Commission report disappoints
The long-awaited report from the Norwegian Law Commission, released last Friday, has shocked and disappointed HIV and human rights advocates in Norway and around the world.
After spending almost two years examining every aspect of the use of the criminal law to punish and regulate people with communicable diseases (with a specific focus on HIV) the Commission has recommended that Norway continues to essentially criminalise all unprotected sex by people living with HIV regardless of the actual risk of HIV exposure and regardless of whether or not there was intent to harm. The only defence written into the new draft law is for the HIV-negative partner to give full and informed consent to unprotected sex that is witnessed by a healthcare professional.
As highlighted in this news story from NAM, low or undetectable viral load will provide no defence to “exposure” charges (although the Commission has recommended that it may be a mitigating fact during sentencing). However, in contrast to the recent Supreme Court of Canada ruling, condoms alone will continue to suffice as a defence.
Given the importance of this report – and its many internal inconsistencies that result in a recommendation for a new law that will actually make it easier to prosecute people with HIV for low- (or no-) risk sex, such as the current oral sex prosecution of Louis Gay – I will be writing a series of stories examining different aspects. In the coming days, there will detailed analysis of the Commissions’ report from Professor Matthew Weait as well as an interview with the dissenting Commission member, Kim Fangen.
|
|
|
Health and Care Services Minister, Jonas Gahr Støre, is presented with the report from Law Commission chair, Professor Aslak Syse on Friday 19th October 2012. (Source: Norwegian Ministry of Health and Care Services) |
Background
Since the first prosecution in 1995, Norway has been using a 110 year-old law to prosecute potential or perceived HIV exposure or HIV transmission, which has the the primary aim of protecting public health.
With the exception of one prosecution each for hepatitis B and hepatitis C transmission, the law has only been used in relation to HIV, and so consequently, paragraph 155 of the Norwegian Penal Code is usually referred to as ‘the HIV paragraph’. There is no consent nor ‘safer sex’ defence in this law, which essentially criminalises all sex by people with HIV.
A new penal code was adopted in 2005 that added a consent defence for “spouses” or other couples living together on a steady basis – and the discussion text further noted that condom use should also be a defence. However, this has not been enacted due to its being roundly criticised by many HIV and human rights groups in Norway and beyond – including by South African Constitutional Court Justice, Edwin Cameron – as being overly draconian and hypocritical given Norway’s role as an arbiter and defender of international human rights.
Consequently, in December 2010, the Norwegian Government appointed a law commission on penal code and communicable diseases to assess whether or not a criminal law was necessary, and if so, what should be criminalised. The Commission consisted of 12 members, including medical and legal practitioners, scientists and academics with backgrounds in sexuality, ethics and human rights, as well as one HIV activist, Kim Fangen.
Kim spoke about the work of Commission – and its potential impact – at the recent international conference on the criminalisation of HIV non-disclosure, potential or perceived HIV exposure and non-intentional HIV transmission that took place in Berlin. The meeting was co-organised by the European AIDS-Treatment Group (EATG), Deutsche AIDS-Hilfe (DAH), the International Planned Parenthood Federation (IPPF), and HIV in Europe.
At the meeting, Kim noted: “It surprised the Commission and many others that people are still being prosecuted under this paragraph [155] when another paragraph was adopted…in 2005. The usual practice in Norway [and elsewhere] is to take into consideration the revised and adopted paragraph even if it’s not yet in force.”
The Commission met twelve times for up to three days at a time, and consulted with national and international experts on HIV and the law along with government representatives, health organisations, and people living with HIV. Some Commission members also participated in the UNAIDS expert meeting on HIV and the criminal law in Geneva, in August/September 2011, as well as the the high level international consultation on HIV and the criminal law held in Oslo in February 2012, which coincided with the Oslo Declaration meeting where two Commission members were present.
In other words, the Commission had every possible opportunity to come up with a report that would result in Norway leading the world in terms of a rational, proportionate, ethical and just response that balances public health with human rights. Instead – with the exception of Kim Fangen – they opted for the most conservative outcome possible, that appears to ignore much of the legal and scientific expertise presented to it, in favour of a law that they believe will act as a deterrent to risky sex and normalise the long-standing Norwegian traditional of promoting monogamous sexual relationships for procreation.
The report
 |
|
The Norwegian Committee report, entitled ‘Of love and cooling towers’ (to reflect the report’s lesser focus on environmental health issues as well as on HIV and other communicable diseases) can be viewed or download here. Click here to read the substantial English summary online. |
As expected, the report is long and detailed, and covers many aspects of regulating issues that have an impact on the public health. A substantial English-language summary is available. I have reproduced a summary (of summaries) of the Commission’s recommendations as they relate to HIV (and ostensibly other sexually transmitted infections) below.
The members of the Commission have divided opinions on whether the person-to-person transmission of infection should be covered by a special penal provision as is the case at present (section 155 of the 1902 Penal Code). One member proposes that this penal provision be repealed and that no new provision be added to the 2005 Penal Code, and that the provision already adopted in the 2005 Penal Code not enter into force.
The 11 other members find it clearly most appropriate to have a separate penal provision on direct and indirect person-to-person transmission of serious communicable diseases, including through sexual intercourse. This is proposed in the draft of section 237 on transmission of infection in the 2005 Penal Code. A separate provision of this nature makes it possible to introduce, in the text of the statute, impunity in cases where responsible behaviour has been displayed in terms of communicable disease control, and to establish rules for when consent will exempt a person from criminal liability. It is proposed that the threat of criminal prosecution should target the act of transmitting a communicable disease that causes significant harm to body or health, as well as blameworthy conduct that results in exposure of another person to the risk of being infected with such a disease.
Of these 11 members, a minority of two is in favour of a penalty only being applicable when infection is transmitted. The other nine members are of the opinion that the act of exposing another person to the risk of infection should also be punishable when the behaviour in question is blameworthy («on repeated occasions or through reckless behaviour») from the perspective of communicable disease control. This is also warranted for evidentiary reasons.
It is proposed that the threat of criminal sanctions for direct and indirect person-to-person transmission of infection should only apply to intentional and grossly negligent acts, contrary to section 155 of the 1902 Penal Code and section 237 of the 2005 Penal Code, which also cover simple negligence. The draft statute states that no penalty is applicable when proper infection control measures (such as use of a condom in connection with sexual intercourse) have been observed. Nor is a penalty applicable in the case of transmission of infection in connection with sexual activity when the person who has been infected or exposed to the risk of infection has given prior consent in the presence of health care personnel in connection with infection control counselling.
The special comments to the draft statute point out that the prosecuting authority should show restraint in cases of infection transmitted from mother to child, in connection with the use of shared injection equipment among drug users, in connection with sex work and between two infected persons, particularly when both of them are aware of their own and their partner’s infection status.
The proposal entails a certain decriminalisation and reduced criminalisation in relation to the current section 155, and a clarification of when penalties are not applicable. It is proposed that the penalty level be reduced somewhat. The current maximum penalty (six years’ imprisonment) is only to be maintained for aggravated transmission of infection, which will primarily apply in cases where the transmission of infection has caused loss of life, the infection was transmitted to two or more persons, or transmitted as a result of “particularly reckless behaviour”.
The report’s recommendations are just that – recommendations – and the final outcome may be very different. The process will take a further 18 months, and won’t be finalised until 2014.
In the coming months, the Ministry of Health and Care Services will, together with the Ministry of Justice and Public Security, thoroughly examine the report and recommendations which is classified as an ONR – Official Norwegian Report.
They will then produce an open hearing letter which will allow for further comment.
All the comments and any additional recommendations will then be taken into consideration before the two Ministries send their final recommendation to the Norwegian Parliament.
It is entirely possible that the Government may ignore these recommendations completely.
 |
|
The Google-translated headline of the Norwegian-language Aftenposten story of July 24 2012 highlighting that two promiment MPs do not want any law that would criminalise potential or perceived HIV exposure or transmission. |
In July, two prominent and influential MPs, Håkon Haugli (Labour) and Bent Høie (Conservative) came out in favour of no replacement for Paragraph 155.
If both parties support their positions, there would be a firm majority in Parliament to ignore the Commission’s recommendation and, instead, to repeal article 155 (and its 2005 replacements) and pass no new law at all.
As the experience of its Nordic neighbour, Denmark, has shown, the sky does not fall in – risky sex and new infections do not increase – when there is no law governing the behaviour of people with HIV, because, as numerous studies have found, the vast majority of people living with HIV are responsible; their behaviour is not influenced by criminal law; and most new infections emanate from undiagnosed HIV.
Lawyers critique Supreme Court ruling
Some criminal lawyers are worried that the Supreme Court has imposed on people prosecuted for not disclosing their HIV-positive status to sex partners a “significant evidentiary burden” to show that they used a condom and that their viral loads were low when they had sex. A pair of decisions handed down on Oct.