A new report published today (May 29th 2019) by the HIV Justice Network on behalf of HIV JUSTICE WORLDWIDE provides clear evidence that the growing, global movement against HIV criminalisation has resulted in more advocacy successes than ever before. However, the number of unjust HIV criminalisation cases and HIV-related criminal laws across the world continue to increase, requiring more attention, co-ordinated advocacy, and funding.
Advancing HIV Justice 3: Growing the global movement against HIV criminalisation provides a progress report of achievements and challenges in global advocacy against HIV criminalisation from 1st October 2015 to 31st December 2018.
Although the full report is currently only available in English, a four-page executive summary is available now in English, French, Russian and Spanish. The full report will be translated into these languages and made available later this summer.
The problem
HIV criminalisation describes the unjust application of criminal and similar laws to people living with HIV based on HIV-positive status, either via HIV-specific criminal statutes or general criminal or similar laws. It is a pervasive illustration of how state-sponsored stigma and discrimination works against a marginalised group of people with immutable characteristics. As well as being a human rights issue of global concern, HIV criminalisation is a barrier to universal access to HIV prevention, testing, treatment and care.
Across the globe, laws used for HIV criminalisation are often written or applied based on myths and misconceptions about HIV and its modes of transmission, with a significant proportion of prosecutions for acts that constitute no or very little risk of HIV transmission, including: vaginal and anal sex when condoms had been used or the person with HIV had a low viral load; oral sex; and single acts of breastfeeding, biting, scratching or spitting.
Our global audit of HIV-related laws found that a total of 75 countries (103 jurisdictions) have laws that are HIV-specific or specify HIV as a disease covered by the law. As of 31st December 2018, 72 countries had reported cases: 29 countries had ever applied HIV-specific laws, 37 countries had ever applied general criminal or similar laws, and six countries had ever applied both types of laws.
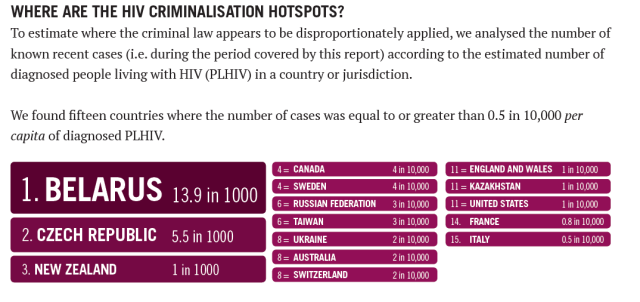
 During our audit period, there were at least 913 arrests, prosecutions, appeals and/or acquittals in 49 countries, 14 of which appear to have applied the criminal law for the first time. The highest number of cases were in Russia, Belarus and the United States. When cases were calculated according to the estimated number of diagnosed people living with HIV, the top three HIV criminalisation hotspots were Belarus, Czech Republic and New Zealand.
During our audit period, there were at least 913 arrests, prosecutions, appeals and/or acquittals in 49 countries, 14 of which appear to have applied the criminal law for the first time. The highest number of cases were in Russia, Belarus and the United States. When cases were calculated according to the estimated number of diagnosed people living with HIV, the top three HIV criminalisation hotspots were Belarus, Czech Republic and New Zealand.
 The pushback
The pushback
Promising and exciting developments in case law, law reform and policy took place in many jurisdictions: two HIV criminalisation laws were repealed; two HIV criminalisation laws were found to be unconstitutional; seven laws were modernised; and at least four proposed laws were withdrawn. In addition, six countries saw precedent-setting cases limiting the overly broad application of the law through the use of up-to-date science.
 The solution
The solution
Progress against HIV criminalisation is the result of sustained advocacy using a wide range of strategies. These include:
- Building the evidence base Research-based evidence has proven vital to advocacy against HIV criminalisation. In particular, social science research has been used to challenge damaging myths and to identify who is being prosecuted, in order to help build local and regional advocacy movements.
- Ensuring the voices of survivors are heard HIV criminalisation advocacy means ensuring that HIV criminalisation survivors are welcomed and supported as advocates and decision-makers at all stages of the movement to end HIV criminalisation.
- Training to build capacity Successful strategies have focused on grassroots activists, recognising that training events must be community owned and provide opportunities for diverse community members to come together, hold discussions, set agendas, and build more inclusive coalitions and communities of action.
- Using PLHIV-led research to build community engagement capacity Research led by people living with HIV (PLHIV) provides a mechanism to engage communities to develop in-depth understanding of issues and build relationships, mobilise and organise.

- Using science for justice HIV criminalisation is often based on outdated and/or inaccurate information exaggerating potential harms of HIV infection. In addition, HIV-related prosecutions frequently involve cases where no harm was intended; where HIV transmission did not occur, was not possible or was extremely unlikely; and where transmission was neither alleged nor proven beyond a reasonable doubt.
- Engaging decision-makers through formal processes Activists have worked to bring about legal and policy changes not only by lobbying local decision-makers, but also by engaging in other formal processes including using international mechanisms to bring HIV criminalisation issues to the attention of state or national decision-makers.
- Acting locally and growing capacity through networks Many community organisations working to limit HIV criminalisation are actively supporting grassroots community advocates’ participation at the decision-making table.
- Getting the word out and engaging with media Activists have employed diverse strategies to extend the reach of advocacy against HIV criminalisation including pushing the issue onto conference agendas, presenting messaging through video, working through digital media forums, using public exhibitions to push campaign messaging, and holding public demonstrations. Sensationalist headlines and misreporting of HIV-related prosecutions remain a major issue, perpetuating HIV stigma while misrepresenting the facts. Activists are endeavouring to interrupt this pattern of salacious reporting, working to improve media by pushing alternative, factual narratives and asking journalists to accurately report HIV-related cases with care.
Acknowlegements
Advancing HIV Justice 3 was written on behalf of HIV JUSTICE WORLDWIDE by the HIV Justice Network’s Senior Policy Analyst, Sally Cameron, with the exception of the Global overview, which was written by HIV Justice Network’s Global Co-ordinator, Edwin J Bernard, who also edited the report.
We would especially like to acknowledge the courage and commitment of the growing number of advocates around the world who are challenging laws, policies and practices that inappropriately regulate and punish people living with HIV. Without them, this report would not have been possible.
 We gratefully acknowledge the financial contribution of the Robert Carr Fund to this report.
We gratefully acknowledge the financial contribution of the Robert Carr Fund to this report.
A note about the limitations of the data
The data and case analyses in this report cover a 39-month period, 1 October 2015 to 31 December 2018. This begins where the second Advancing HIV Justice report – which covered a 30-month period, 1 April 2013 to 30 September 2015 – left off. Our data should be seen as an illustration of what may be a more widespread, but generally undocumented, use of the criminal law against people with HIV.
Similarly, despite the growing movement of advocates and organisations working on HIV criminalisation, it is not possible to document every piece of advocacy, some of which takes place behind the scenes and is therefore not publicly communicated.
Despite our growing global reach we may still not be connected with everyone who is working to end HIV criminalisation, and if we have missed you or your work, we apologise and hope that you will join the movement (visit: www.hivjusticeworldwide.org/en/join-the-movement) so we can be in touch and you can share information about your successes and challenges.
Consequently, this report can only represent the tip of the iceberg: each piece of information a brief synopsis of the countless hours and many processes that individuals, organisations, networks, and agencies have dedicated to advocacy for HIV justice.
Suggested citation: Sally Cameron and Edwin J Bernard. Advancing HIV Justice 3: Growing the global movement against HIV criminalisation. HIV Justice Network, Amsterdam, May 2019.
 urpose of this critical media toolkit is to inform and equip global grassroots advocates who are engaged in media response to HIV criminalisation–and to demystify the practice of working with, and through, media to change the conversation around criminalisation.
urpose of this critical media toolkit is to inform and equip global grassroots advocates who are engaged in media response to HIV criminalisation–and to demystify the practice of working with, and through, media to change the conversation around criminalisation. ment with media to change narratives around this unjust practice.
ment with media to change narratives around this unjust practice. Positive Women’s Network – USA (PWN-USA), the HIV JUSTICE WORLDWIDE Steering Committee member organisation that produced the toolkit, has been working on HIV criminalisation for many years, and was an instrumental part of the coalition that brought HIV criminal law reform to the US state of California.
Positive Women’s Network – USA (PWN-USA), the HIV JUSTICE WORLDWIDE Steering Committee member organisation that produced the toolkit, has been working on HIV criminalisation for many years, and was an instrumental part of the coalition that brought HIV criminal law reform to the US state of California.



