Beyond Blame: Challenging HIV Criminalisation
A pre-conference meeting for AIDS 2014
In July 2014, at a meeting held to just prior to the International AIDS Conference in Melbourne, Australia around 150 participants from all regions of the world came together to discuss the overly broad use of the criminal law to control and punish people living with HIV – otherwise known as ‘HIV criminalisation’.
The meeting was hosted by Living Positive Victoria, Victorian AIDS Council/Gay Men’s Health Centre, National Association of People Living with HIV Australia and the Australian Federation of AIDS Organisations, with the support of AIDS and Rights Alliance of Southern Africa, Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network, Global Network of People Living with HIV, HIV Justice Network, International Community of Women Living with HIV, Sero Project and UNAIDS.
The meeting was financially supported by the Victorian Department of Health and UNAIDS.
This highlights video (12 mins, 50 secs) was directed, filmed and edited by Nicholas Feustel, with interviews and narration by Edwin J Bernard. The video was produced by georgetown media for the HIV Justice Network.
Download the highlights video from:http://vimeo.com/hivjustice/beyondblame
Below is a feature story based on the transcript of the highlights video, with additional links and information. You can also read Felicita Hikuam’s excellent (and remarkably quickly-written) summary of the day in ‘Mujeres Adelante’ and Daniel Reeders’s impressive collection of tweets from the meeting.
FEATURE STORY
A day to come together, find solutions, and move forward

Paul Kidd: On behalf of Living Positive Victoria, the Victorian AIDS Council, Australian Federation of AIDS Organisations, and the National Association of People with HIV Australia, welcome to Beyond Blame: Challenging HIV Criminalisation. We hope today’s event is inspiring and productive and that it kicks off the discussion about HIV criminalisation that will continue through the week and beyond.

Edwin Bernard: I think this is the largest HIV Criminalisation Pre-Conference to date at an International AIDS Conference. So the idea of the meeting is to bring people together. People who are working on this issue, who are interested in learning more about it, and we’re going to really work hard to come together, find solutions, and move forward.
Julian Hows: GNP+ has been involved in this issue of criminalisation since 2002, 2003, when we noticed an increase in the rates of prosecution in Europe effectively and started the first scan of the 53 signatory countries of the European Convention on Human Rights.
This has since become the Global Criminalisation Scan, an international ‘clearing-house’ of resources, research, and initiatives on punitive laws and policies impacting people living with HIV.

Jessica Whitbread: And ICW are really, really excited to be here and part of this. Criminalisation is a huge issue for us. Over 50% of people living with HIV are women and many of these laws initially and still continue to be created as a way to protect women when actually they put us more at risk.
Getting the criminal law changed and out of the HIV response
The meeting began with a surprise announcement by the Minister of Health for Victoria, David Davis, about Australia’s only HIV-specific criminal law, Section 19A of the Victorian Crimes Act. Read more about the campaign to reform the law here.

David Davis: And as a further step in our efforts to reduce the impact of HIV and reduce stigma and discrimination, the coalition government will amend section 19A of the Crimes Act 1958 to ensure that it is non-discriminatory.
Following the announcement Victoria’s Shadow Health Minister, Gavin Jennings, committed to removing (and not just amending) Section 19A within the next 12 months, should Labor win the state election in November.
A keynote address by the Honourable Michael Kirby, a former Justice of the High Court of Australia, and a member of the Global Commission on HIV and the Law, reminded us why an overly broad criminal justice apporach to prevention does more harm than good.

Michael Kirby: In the big picture of this great world epidemic, the criminal law has a trivial role to play. What is most important is getting the law changed and out, not getting the law into the struggle against HIV and AIDS.
The Iowa example: laws are subject to change and should be subject to change
The meeting then focused on Iowa in the United States where both law reform and judicial rulings have limited the overly broad use of the criminal law.

Matt McCoy: You know, in Iowa, we had a very bad law on the books, but it’s not unlike a lot of other places in the country in the United States and in the world. So there was no need for transmission, and with it, the penalty was so extreme, a mandatory lifetime sex offender registry and 25 years in prison.
Watch the video that Senator McCoy showed at the meeting explaning how law reform in Iowa happened.

Sean Strub: Iowa is a conservative farm-belt state. And the effort there began with a small group of people with HIV who started organising others with HIV and educating their own communities and then educating public health officials and reframing the issue in terms of a public health issue rather than simply an issue of justice for people with HIV. Last month, we held a conference at Grinnell College in Grinnell, Iowa. It was the first national conference on HIV criminalisation in the US. The Friday before our conference began, Governor Branstad in Iowa signed a criminalisation reform measure and made Iowa the first state in the United States to subtantively reform and modernise their statute.
Two videos of the HIV Is Not A Crime conference (also known as the Grinnell Gathering) are available. One shows the opening ceremony and can be viewed on the Sero website. A second video highlights the voices of US HIV criminalisation survivors featured at the meeting, and can be viewed on the Sero website.

Nick Rhoades: About a week after the conference was over, the timing was just a little bit off, nonetheless, it’s fantastic. My conviction was overturned by the Iowa Supreme Court. Yeah. Thank you… It’s kinda groundbreaking, their decision, and I, first of all, think that it’s going to have an effect beyond Iowa’s borders, but it basically said that there has to be more than a theoretical chance of transmission to be prosecuted under the law. And previously, that’s not been the case. Basically, it was just if you didn’t disclose, and you had sex, that that would be enough to convict someone. So, for the first time, they basically said that factors such as using protection, being on antiretroviral medication, having an undetectable viral load specifically, should affect whether or not prosecution is able to happen.
Senator McCoy took the opportunity to urge parliamentarians to rethink how they treat HIV in a criminal context.
Matt McCoy: Many of these laws went into effect in the United States during the AIDS crisis and the scares that society had around the issue, and in many cases they were put into effect using a one-size-fits-all measure. And so this is a great opportunity to go back and to revisit that and to realise that our laws are subject to change and should be subject to change.
Science can change laws and limit prosecutions
A number of countries in Europe have also recently revisited their criminal laws, policies or practices. A poster, Developments in criminal law following increased knowledge and awareness of the additional prevention benefit of antiretroviral therapy, presented at AIDS 2014 by the HIV Justice Network, showed where and how this has taken place.
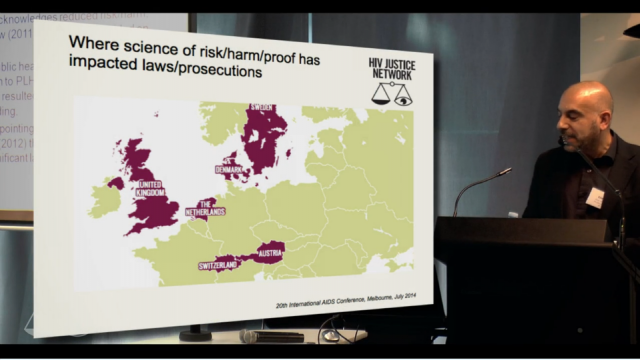
Edwin Bernard: We have to salute the Netherlands, the very first place in the world that actually, way before the Swiss statement, between 2004 and 2007, managed to change the application of the law through a variety of Supreme Court rulings, but also because of advocacy that happened with advocates and healthcare workers and people in the community who limited the role of the criminal law to only intentional exposure or transmission. Denmark was the only country in Western Europe that had an HIV-specific criminal law, and a huge amount of advocacy went on behind the scenes and that law was suspended in 2011 based on the fact that the law was about a serious, life-threatening illness, and the reality was that in Denmark, people living with HIV have exactly the same life expectancy as people without HIV. And so the law just couldn’t apply anymore. And so, we hope that the places like Denmark and the Netherlands will provide inspiration for the rest of us.
Urgent need to focus on global South
But with two-thirds of all HIV-specific criminal laws enacted in the global South, there is now an urgent need to re-focus our efforts.

Patrick Eba: For a long time, we have been saying that there is no prosecution happening in the Global South, particularly in Africa, because we were lacking the information to be able to point to those instances of criminalisation. In fact, there is a lot of prosecution that is happening, and in the past year, if you look at the data that is being maintained by the HIV Justice Network, it is clear. We’ve seen the case in Uganda. We know of a decision that came out some time late last year in South Africa. We know of a number of cases in Kenya, in Gabon, in Cameroon [and especially in Zimbabwe]; and these really show that where we celebrate and are able today to know what is happening in the Global North, our lack of understanding of the situation in the Global South is one that requires more attention.

Dora Musinguzi: Uganda is right now grappling with lots of human rights and legal issues, and it’s going to be such a high climb to really convince our governments, our people, government agencies to make sure that we really have this reform of looking at HIV from a human rights angle, public [health] angle, gender justice angle, if we are going to achieve the gains that we have known to achieve as a country. …But we stand strong in this, we are not giving up. We are looking to a future where we shall challenge this criminalisation, and we hope to come back with a positive story.
Workshops on advocacy messages, science and alternatives to a punitive criminal justice approach
After the morning plenary sessions, participants then attended one of three workshops. The first workshop explored how to get advocacy messages right, in terms of what arguments need to be delivered by whom and to whom.

Laurel Sprague: We talked about the importance of stories. In particular, the stories of people who have been prosecuted, both because of the dignity it gives them to be able to share their own experience, and also because what we’re seeing is so broadly understood to be disproportionate once the details come out.
Laurel’s rapporteur notes can be downloaded in full here. For an example of advocacy messagaging aimed at communities impacted by HIV see this video from Queensland Positive People.
A second workshop highlighted the way that up-to-date science on HIV-related risks has limited the application of the criminal law in Sweden and Canada.

David Mejia-Canales: Really mobilising their scientists, their researchers and really connecting with the lawyers, the judiciary, the prosecutors and putting to them the best evidence that they have.
Download the Powerpoint presentation given by Cecile Kazatchine of the Canadian HIV/AIDS Legal Network here.
The third workshop examined alternatives to a punitive criminal justice system approach, and the risks and benefits of using, for example, public health law or restorative justice.

Daniel Reeders: So if someone shows up at a police station or talks to their doctor about being exposed or infected with HIV, a restorative justice approach would talk about giving them an opportunity to work that issue through with the person who they are otherwise trying to report, either for criminal prosecution or public health management. It acknowledges that people experience HIV infection as an injury and that there is a lack of a process offering them an opportunity to heal.
Daniel’s entire rapporteur report can be read on his blog.
Going home with more ideas and tools and inspiration to continue our work
As the meeting came to a close participants appreciated the day as a rare and much needed opportunity to discuss advocacy strategies.
Paul Kidd: What a day! It is just so amazing to be in this room with all of these incredible people and the sense you have of how much passion and energy and commitment there is around this issue.

Richard Elliott: Even as we face numerous setbacks in our own context sometimes, we see that in fact people are making breakthroughs elsewhere and then that helps us put pressure domestically on decision makers, on legislators, on judges.

Michaela Clayton: It’s important to learn from how people have achieved successes and what have been peoples’ problems in achieving successes in different countries in addressing criminalisation. So for us it’s a wonderful opportunity to learn from others.
Dora Musinguzi: I was encouraged to know that the struggle is not only for us in Africa, in Uganda, and I was also encouraged to know that our colleagues have made progress, and so we can.
Sean Strub: I think everywhere that there is an effort for this advocacy for reform, it is a constantly evolving effort. And the fact that the HIV Justice Network and others brought together this global community which is incredibly mutually supportive. I think of any aspect of the epidemic, I can’t think of an area where there is more collegiality and mutual respect than those of us who’ve centered our work around criminalisation reform. That’s what we’re seeing here in Melbourne, just an expansion of that, and all of us going home with more ideas and tools and inspiration to continue our work.
To remain connected with the global advocacy movement against overly broad HIV criminalisation, like us on Facebook, follow us on Twitter and sign the Oslo Declaration on HIV Criminalisation to join our mailing list.
















