The British HIV Association (BHIVA) and the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) have produced updated guidance on HIV Transmission, the Law and the Work of the Clinical Team.
This guidance is aimed at those working in the field of HIV medicine, especially clinicians, but will also be of use to general practitioners and people living with HIV who want to understand the legal and medical basis for some of their care decisions.
The guidance begins with a clear statement against HIV criminalisation:
BHIVA and BASHH believe that this use of the law is unhelpful and potentially harmful to public health and support UNAIDS recommendations to limit the use of criminal law and the Oslo declaration view that a “non-punitive, non-criminal HIV prevention approach” is preferable.
Covering the law in England & Wales as well as Scotland, the document aims to provide information and guidance on managing issues related to sexual transmission of HIV based on current scientific evidence. It applies generic ethical and professional principles but with a greater emphasis on providing a confidential environment in which extremely sensitive matters can be frankly and fully discussed. This enables appropriate care of people with HIV and benefits public health by encouraging individuals to access testing and treatment. Within this framework this document sets out the roles and responsibilities of health care professionals when caring for individuals living with HIV.
Consistent with the recent BHIVA and the Expert Advisory Group on AIDS (EAGA) position statement on the use of antiretroviral therapy to reduce HIV transmission, the guidance notes:
In most situations the appropriate use of antiretroviral treatment is at least as effective as condoms in preventing sexual transmission of HIV. This is accepted by the [Crown Prosecution Service of England and Wales] and [Scottish Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service] so it is likely that evidence showing that the defendant was taking effective antiretroviral treatment at the time of the alleged transmission may be used to demonstrate that they were not reckless.
The guidance also clearly states that healthcare professionals “must be mindful of their duty not to work beyond their expertise in legal matters. For people with HIV, advice must include the routes of HIV transmission and how to prevent transmission, with information about safer sexual practices, the use of condoms and suppression of viral load. Advice must be given in a non-judgmental way.”
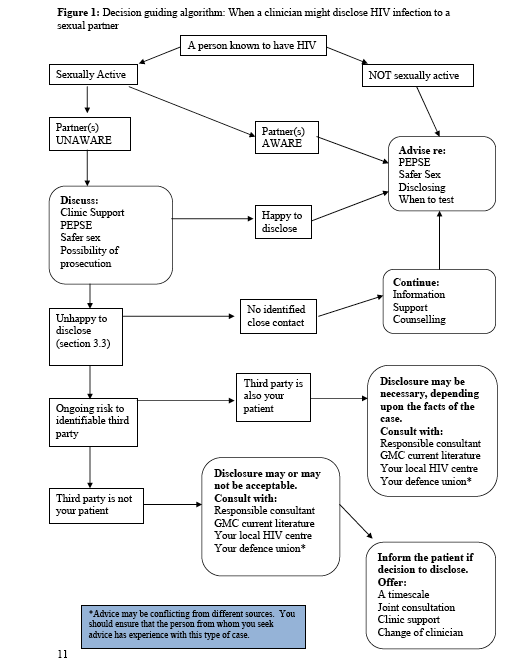
It also discusses issues of confidentiality, noting that “it is important when considering breaching confidentiality to weigh up all potential harms as there may be situations where disclosure of HIV status to protect a sexual partner results in considerable harm to an individual e.g. domestic violence. In situations where a health care professional believes that an HIV positive individual continues to put sexual contacts at risk their duties and subsequent action depend upon the type of contact.” See Figure 1 below.
The guidance also clearly states that “no information should be released to the police unless patient consent has been verified or there is a court order in place, except in very limited circumstances defined by the [General Medical Council].”
Importantly, it also notes that only individuals can make complainants to the police “and health care workers should remain impartial during discussions with patients.”
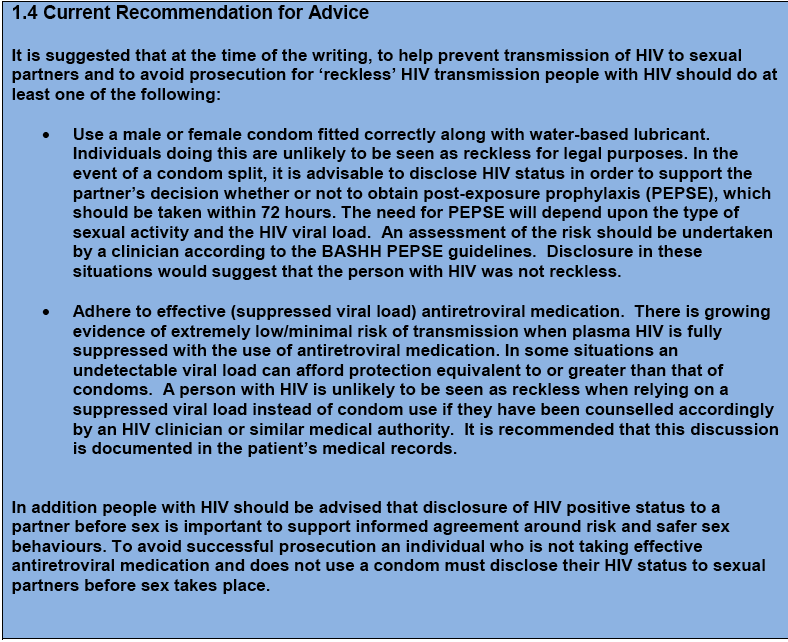
Finally, it provides clear advice to both help prevent transmission of HIV to sexual partners and to avoid prosecution for ‘reckless’ HIV transmission. Accordingly, people with HIV should do at least one of the following:
- Use a male or female condom fitted correctly along with water-based lubricant. Individuals doing this are unlikely to be seen as reckless for legal purposes. In the event of a condom split, it is advisable to disclose HIV status in order to support the partner’s decision whether or not to obtain post-exposure prophylaxis (PEPSE), which should be taken within 72 hours. The need for PEPSE will depend upon the type of sexual activity and the HIV viral load. An assessment of the risk should be undertaken by a clinician according to the BASHH PEPSE guidelines. Disclosure in these situations would suggest that the person with HIV was not reckless.
- Adhere to effective (suppressed viral load) antiretroviral medication. There is growing evidence of extremely low/minimal risk of transmission when plasma HIV is fully suppressed with the use of antiretroviral medication. In some situations an undetectable viral load can afford protection equivalent to or greater than that of condoms. A person with HIV is unlikely to be seen as reckless when relying on a suppressed viral load instead of condom use if they have been counselled accordingly by an HIV clinician or similar medical authority. It is recommended that this discussion is documented in the patient’s medical records.
In addition people with HIV should be advised that disclosure of HIV positive status to a partner before sex is important to support informed agreement around risk and safer sex behaviours. To avoid successful prosecution an individual who is not taking effective antiretroviral medication and does not use a condom must disclose their HIV status to sexual partners before sex takes place.
The entire guidance is reproduced below.